gbXML¶
Green Building XML (gbXML) is a file format designed for interoperability between CAD and building simulation software. More information about gbXML can be found here.
The Tas 3D modeller can import and export gbXML files.
When importing gbXML files in Tas, the 3D modeller will identify common problems with gbXML files and automatically repair many of them making it an incredibly powerful BIM tool.
Note
If you re-import a gbXML file to update the geometry, any edits you have made to the imported model will be preserved and automatically applied to the new model.
Pre-requisites¶
Before you produce a gbXML file from your chosen package to import into Tas, it is important to ensure your model has been setup to produce good quality gbXML files.
If you are exporting a gbXML file from Revit, please see our Revit gbXML Guide for advice regarding how to correct common mistakes with Revit models that may make them unsuitable for energy analysis.
Importing gbXML¶
A gbXML file can only be imported into a new 3D modeller file that does not contain any existing geometry.
To import a gbXML file, go to Import >> Models >> gbXML in the ribbon:
Select your gbXML file and press open. You’ll then be presented with the gbXML Import Report, the gbXML Import Options dialog and a Preview View of your gbXML file.
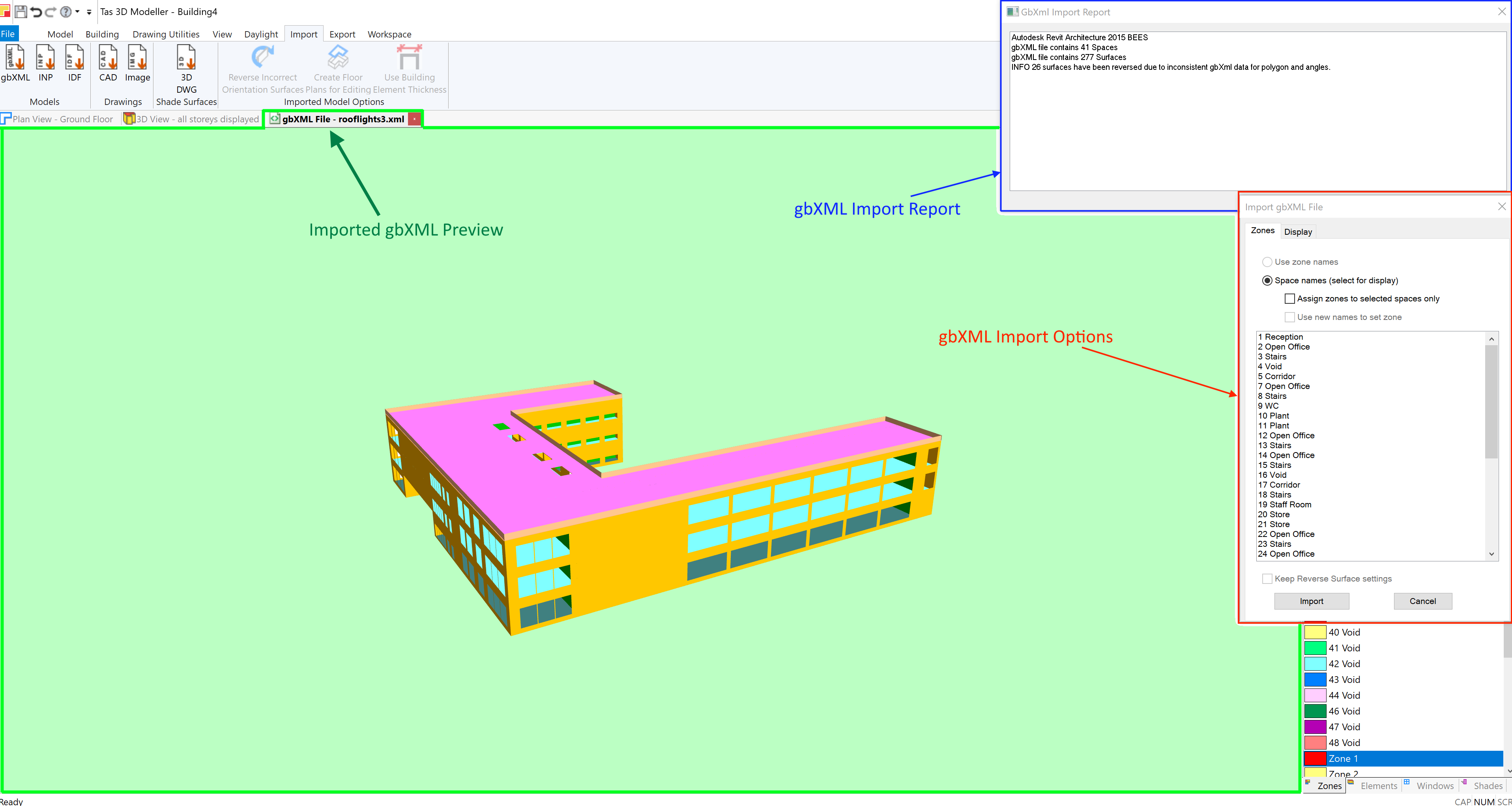
The Import Report contains information such as:
The source of the gbXML file
The number of identified spaces
The number of identified surfaces
Automatic corrections/repairs made by the 3D modeller
At this stage you should check that the number of spaces found in the gbXML file match your expectations.
You should also use the Display tab in the gbXML Import Options to alter the gbXML Preview View to make it easier to visually inspect the model.
Once you have inspected the gbXML Preview, press Import to complete the process.
Warning
It is very important to inspect the model for import errors and artifacts. If there are errors in your model, consult the documentation for the software producing the gbXML file. If you are using Revit, see our Revit gbXML training material in addition to the Revit documentation.
Display Options¶
The following gbXML display options are available prior to completing the gbXML import process:
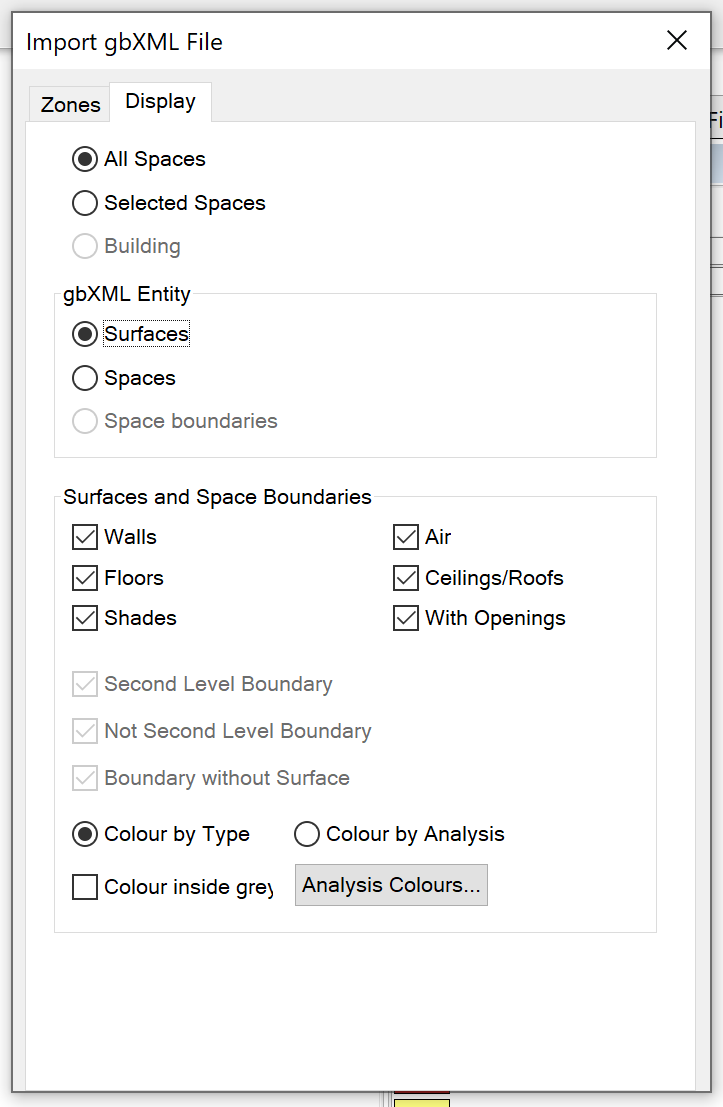
The gbXML Entity option allows you to switch between viewing the surfaces in the gbXML file and the spaces:
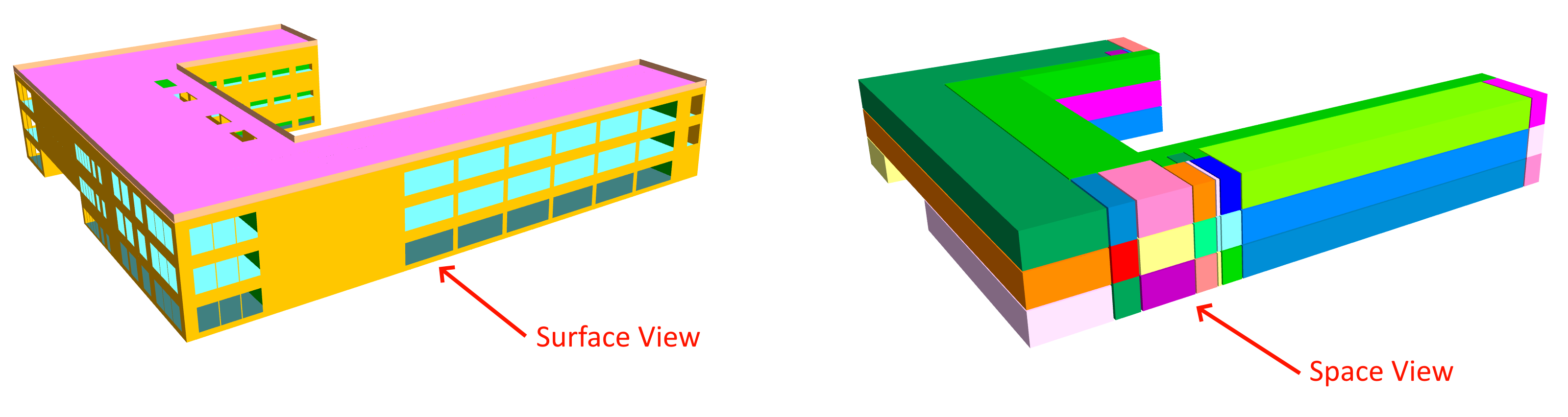
Using these options you can check for missing surfaces, extra/misshapen surfaces and incomplete spaces. Usually there should be no gaps between adjacent spaces.
When you have the Surfaces displayed, you can also alter the Surface and Space Boundary display options. You can examine each of the following options in isolation:
Walls
Floors
Shades
Air
Ceilings/Roofs
With Openings
This will allow you to check that the expected elements are in the correct place, and there are no unexpected air gaps.
You can use the Colour inside grey option to quickly visually identify surfaces which have an incorrect orientation – if you see grey on the outside of any surfaces, the orientation of those surfaces are incorrect.
You can also colour by Analysis Colours, which will allow you to identify surfaces corresponding to the following elements:
Ground Floor
Exposed
Internal
Link
Adiabatic
gbXML Shades
If any of the surfaces have the wrong types assigned in the gbXML file and you do not have the ability to correct the source and re-export, the building element types can be re-assigned in the 3D modeller after importing the gbXML file. If you update the gbXML file and need to re-import it, these changes will be preserved and applied to the newly imported model.
gbXML vs Tas3D Geometry¶
When working with gbXML imports rather than purely native Tas3D geometry, there are some differences it is useful to be aware of.
Firstly, by default, there is only a single 3D view. Though there are storeys, there are no floor plans and therefore no 2D plan views:
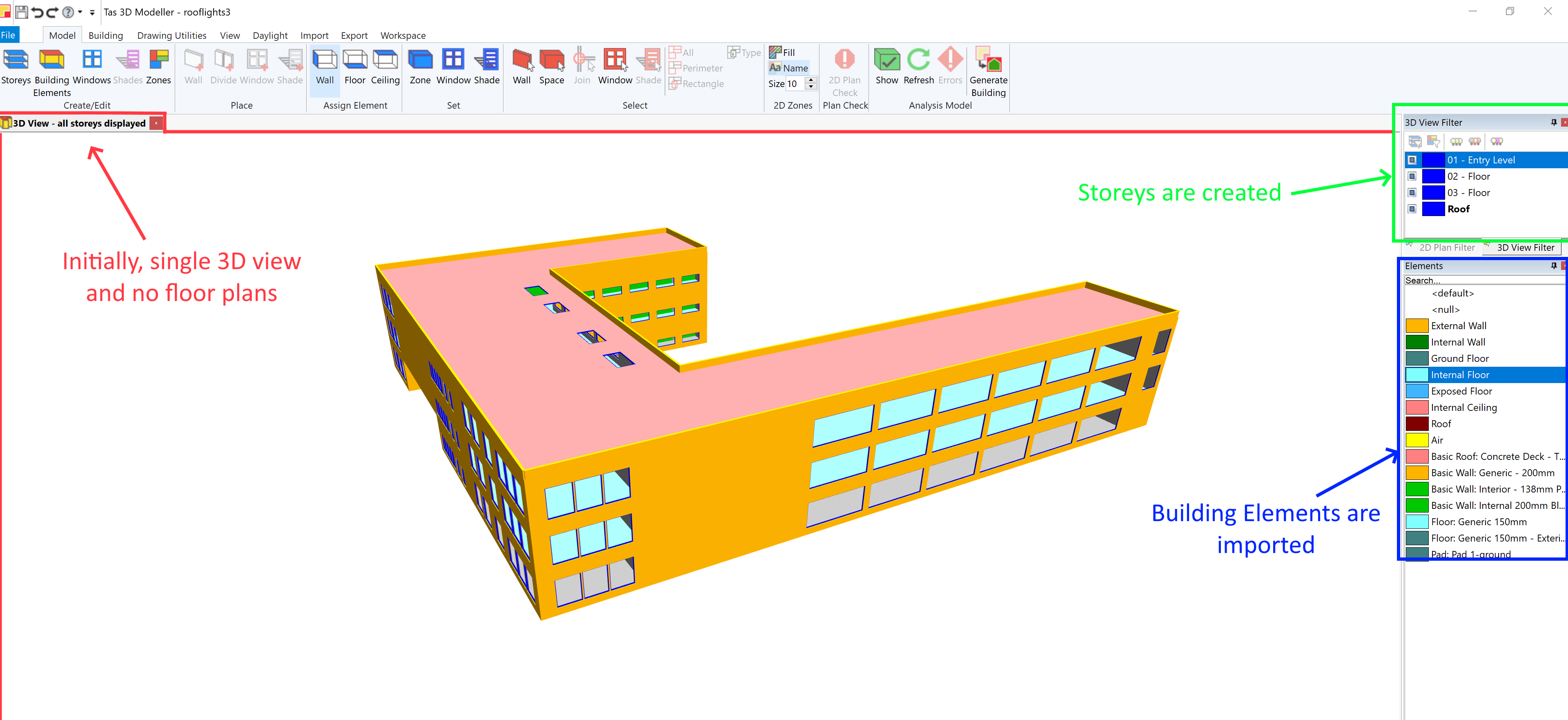
This means if you wish to re-assign surfaces Building Elements, you’ll need to do so in the 3D view unless you create floor plans for editing.
This also means you cannot change the positions of imported walls, floors and ceilings or delete them - though you can create more.
Creating Floor Plans¶
You can create 2D floor plans for editing for a gbXML imported model. This will allow you to:
View zones in 2D
View daylight results
Add zones to the model
Assign tags to zones
Add walls & therefore simple internal shades
To create a gbXML editable 2D floor plan, go to Import >> Imported Model Options >> Create Floor Plans for Editing in the ribbon:
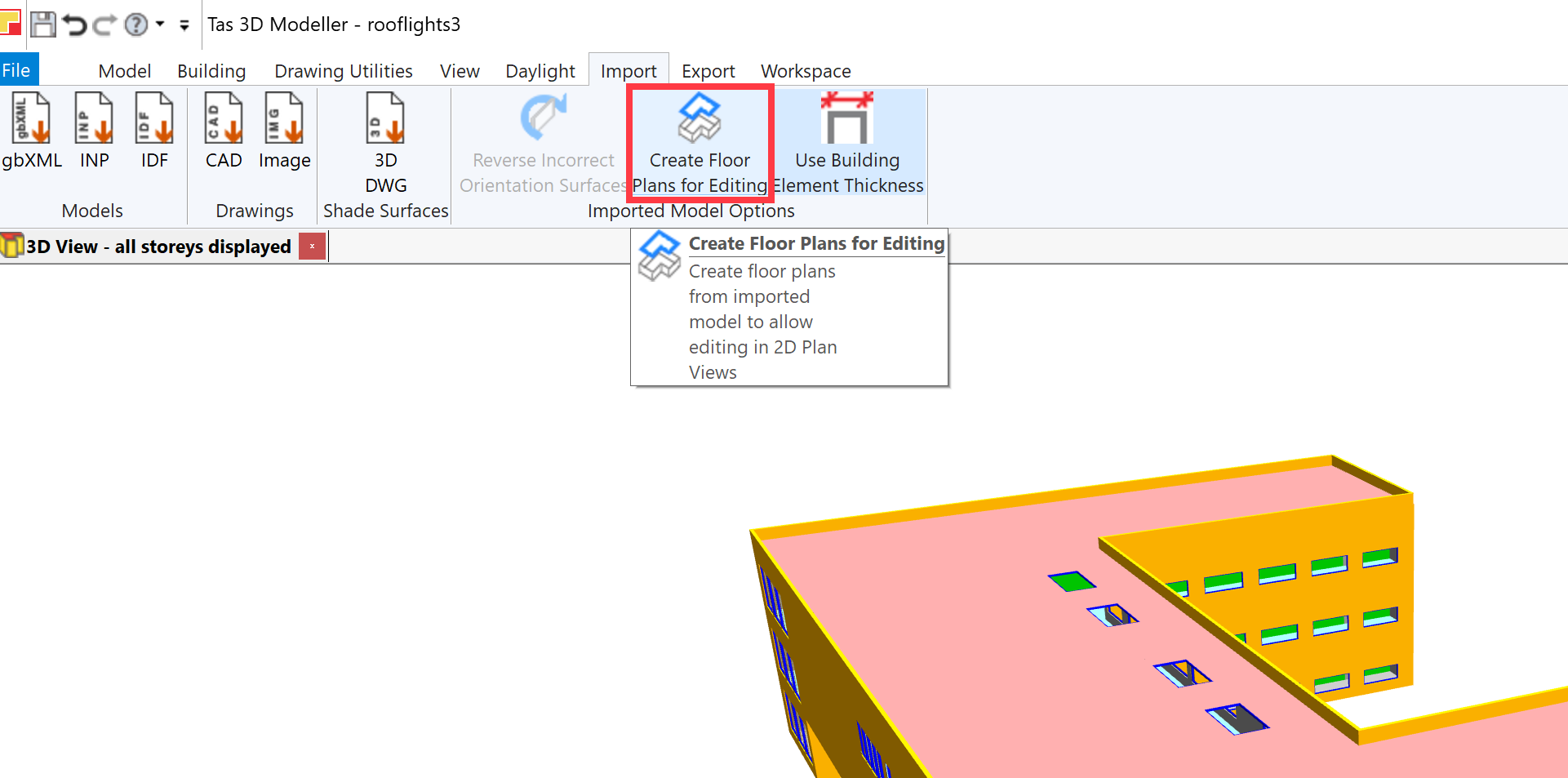
After pressing this button, you can then create 2D views to display the newly created floor plans. Previously, this button was disabled:
Note
You can only add internal walls to an editable plan view. For external walls, create a regular storey.
You can also create regular storeys in the 3D modeller, which are empty by default. These can be used to create (external) zones for shading purposes.
Adding Zones¶
Additional zones can be added to an imported gbXML model by sub-dividing an imported space:
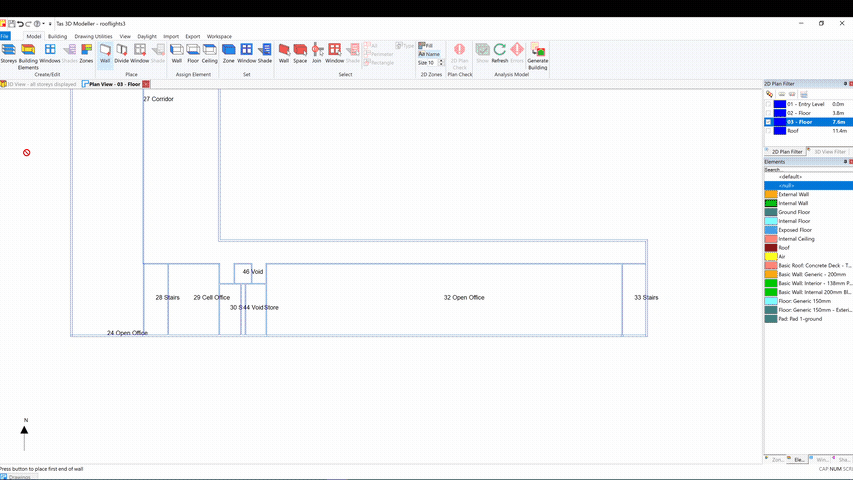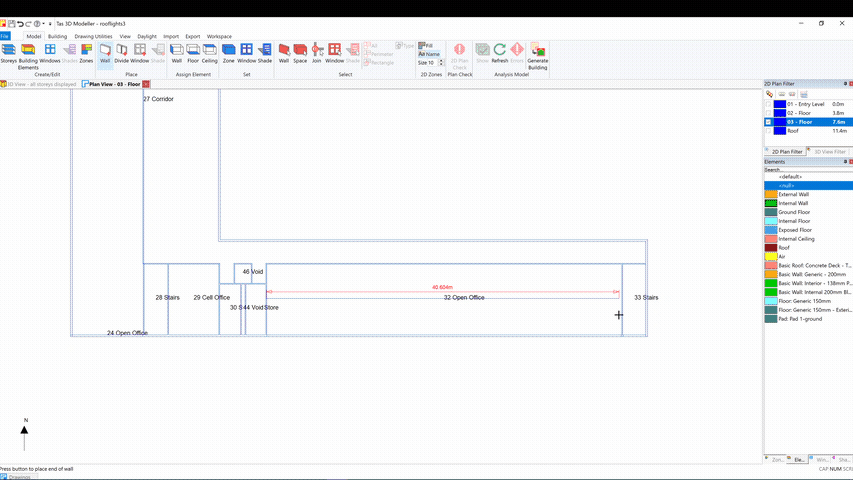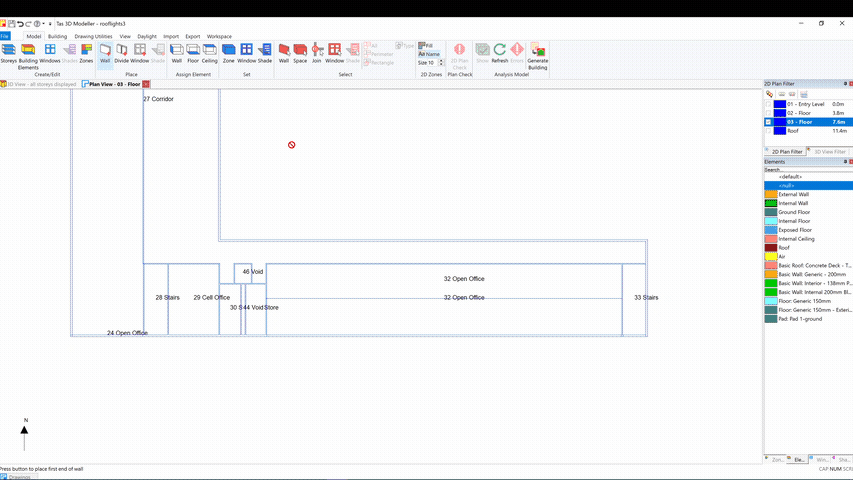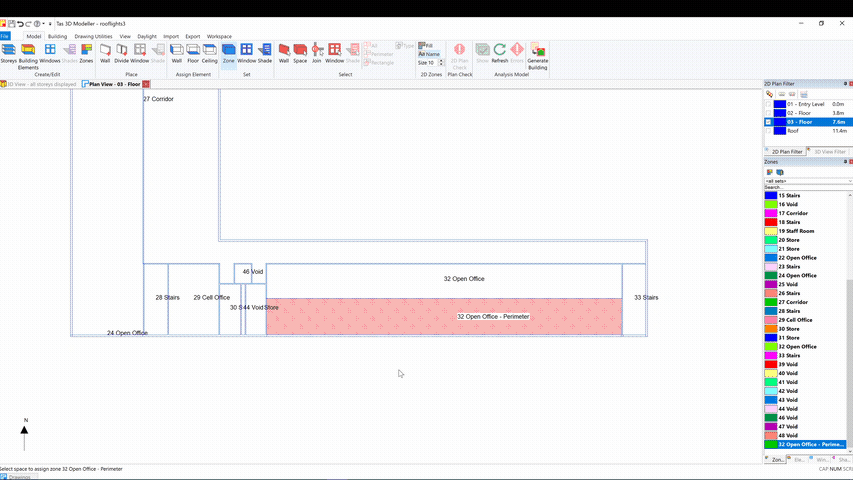
This is particularly useful if you need to add perimeter zoning as required by the EPC conventions.
Shades¶
There are three main types of shades that can be added to a Tas3D model:
Simple Shades (e.g. for windows, brise soleils)
Shade Buildings
3D Shade Surfaces (from a 3D DWG)
Simple Shades¶
Simple shades can be added to the imported gbXML geometry by creating an external zone adjacent to the external fascade using null walls.
Note
Simple external shades cannot be added to editable gbXML floor plans.
After creating a new storey, switch to the 3D view and select a wall to which you wish to add a shade. Right click, and click Copy Null to Storey:
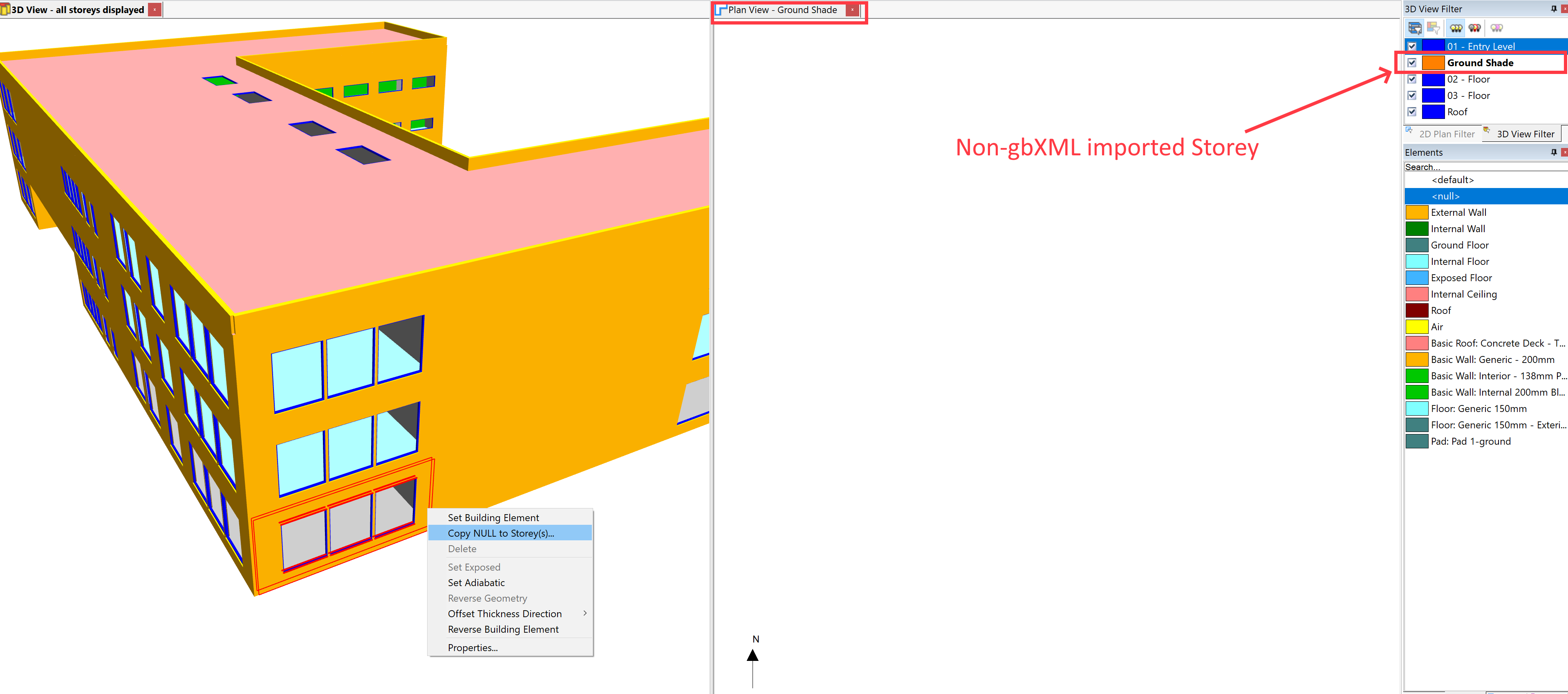
Select a regular storey – that is, a storey that wasn’t created as part of the gbXML import process. This will create a null wall in the 2D plan, which you can add further walls to in order to create an external zone:
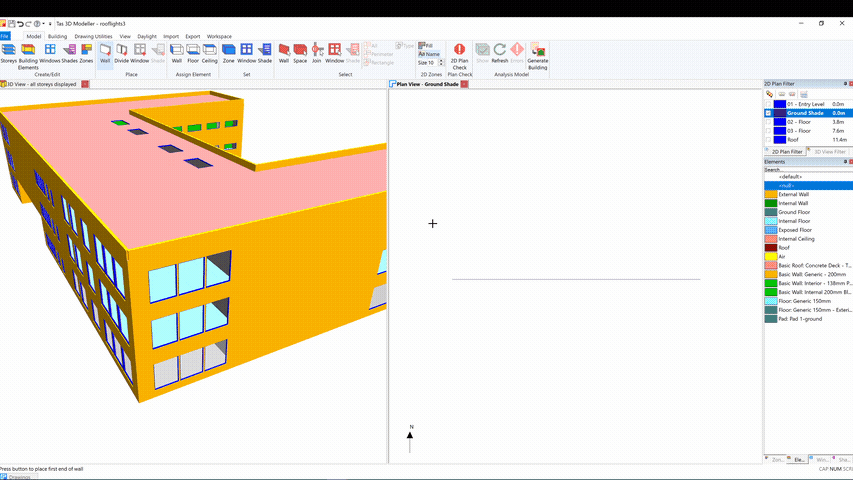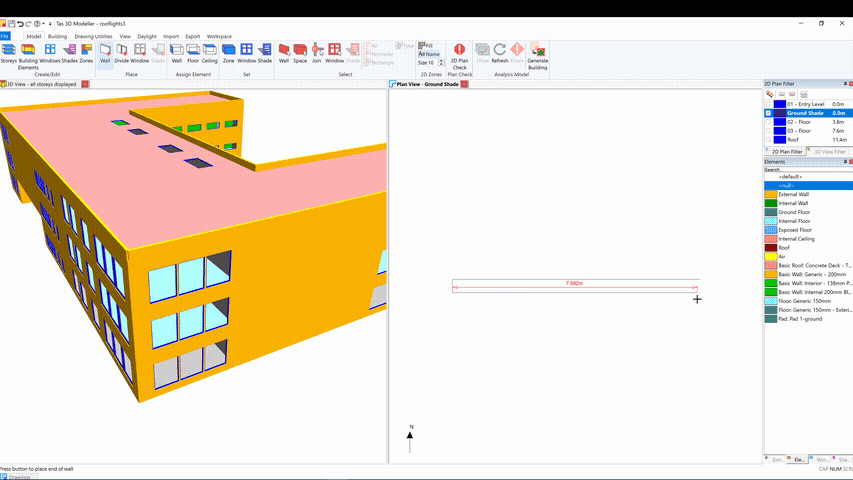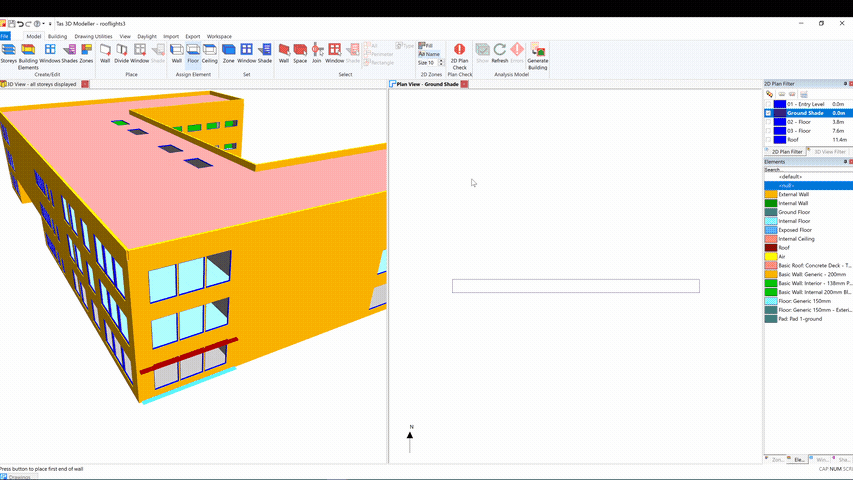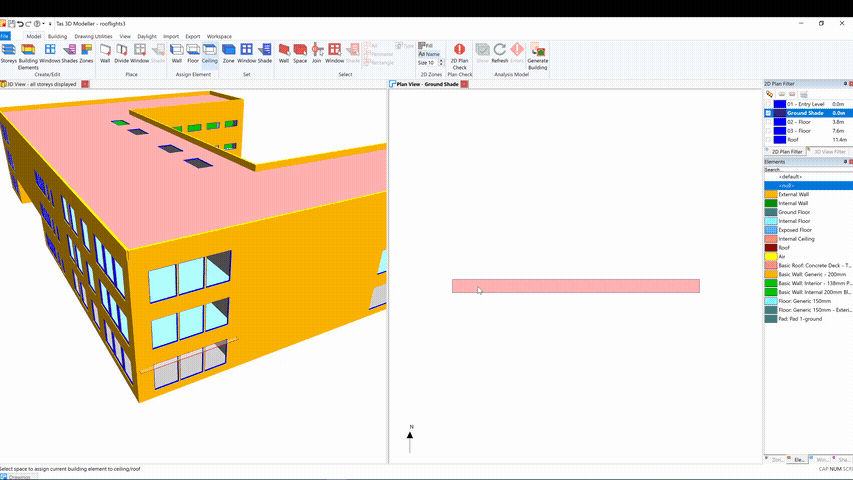
You can then zone the space, set the floor and ceiling building elements to null and place a shade:
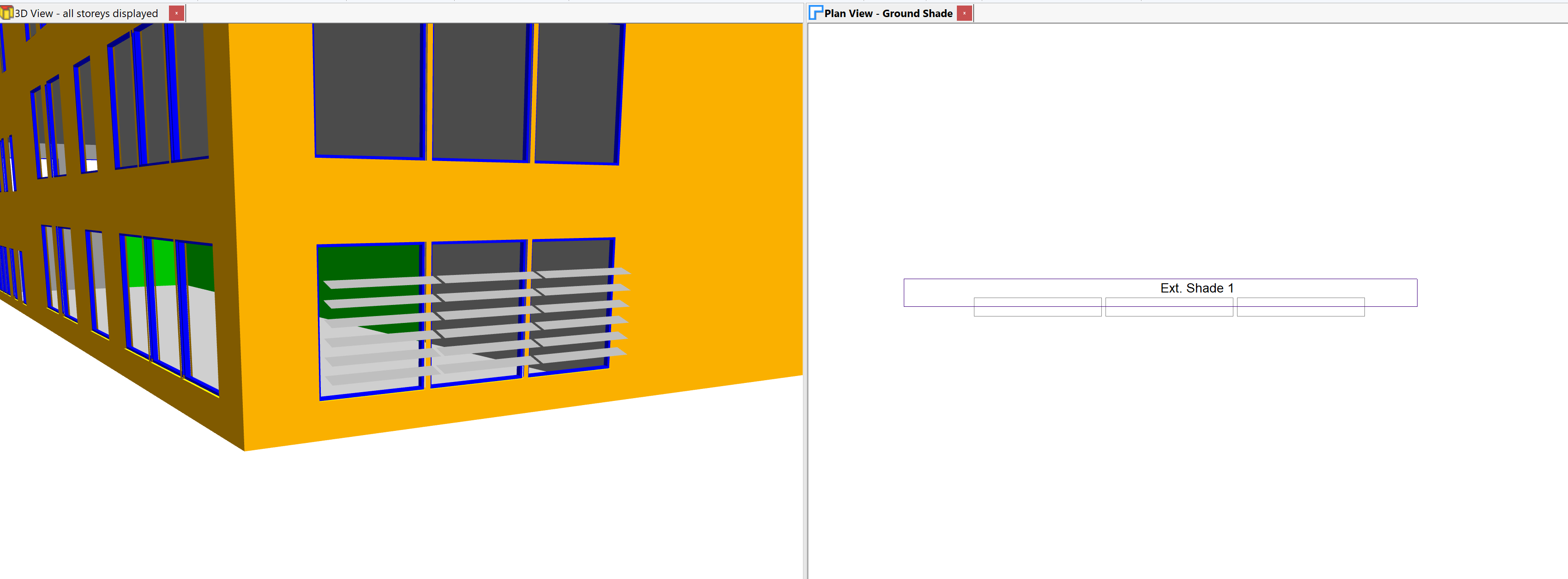
For more information about creating simple shades, see Shades.
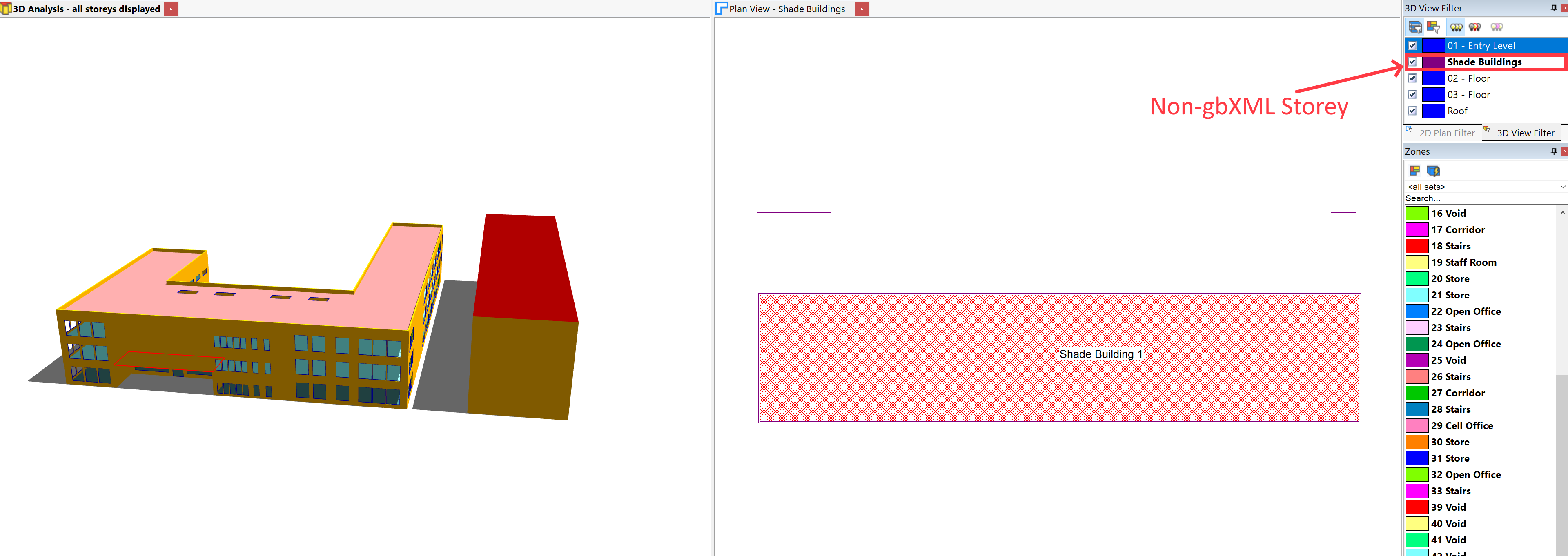
Shade Buildings¶
If you do not have a regular Storey in your Tas3D file, create one.
Shade Buildings can then be added to a gbXML file in the same way as you would with a non-gbXML imported Tas3D file:
3D Shade Surfaces¶
A 3D DWG file containing 3D geometry can be imported into both a regular Tas3D file and a Tas3D file containing gbXML imported geometry.
This is useful when modelling complex shading systems that may not be included in the gbXML export produced by other software.
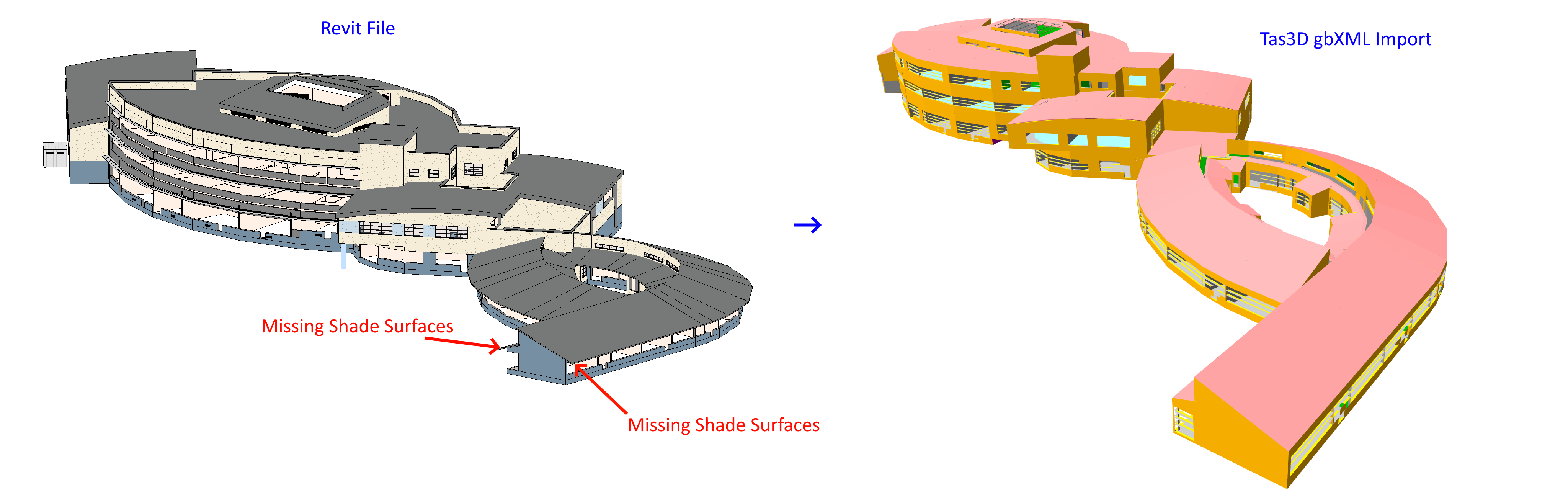
To import the missing shade surfaces in this case, we can use a 3D DWG containing those missing surfaces:
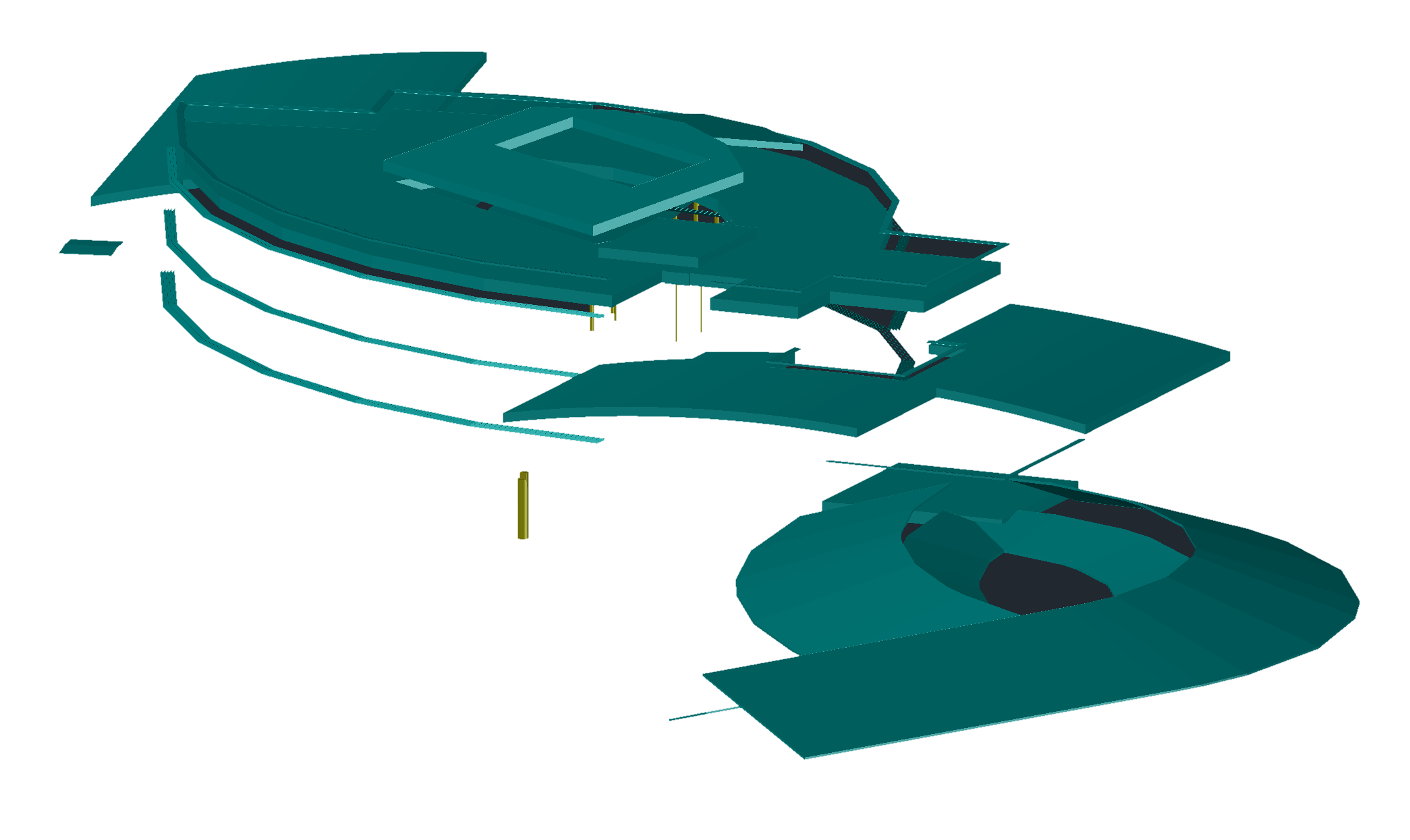
Autocad drawing exported from Revit showing only the missing shade surfaces from the gbXML file.¶
In the 3D modeller, after importing the gbXML file, press the Import DWG button:
Select the 3D DWG and press OK. You will then be presented with a preview of the DWG and some import options:
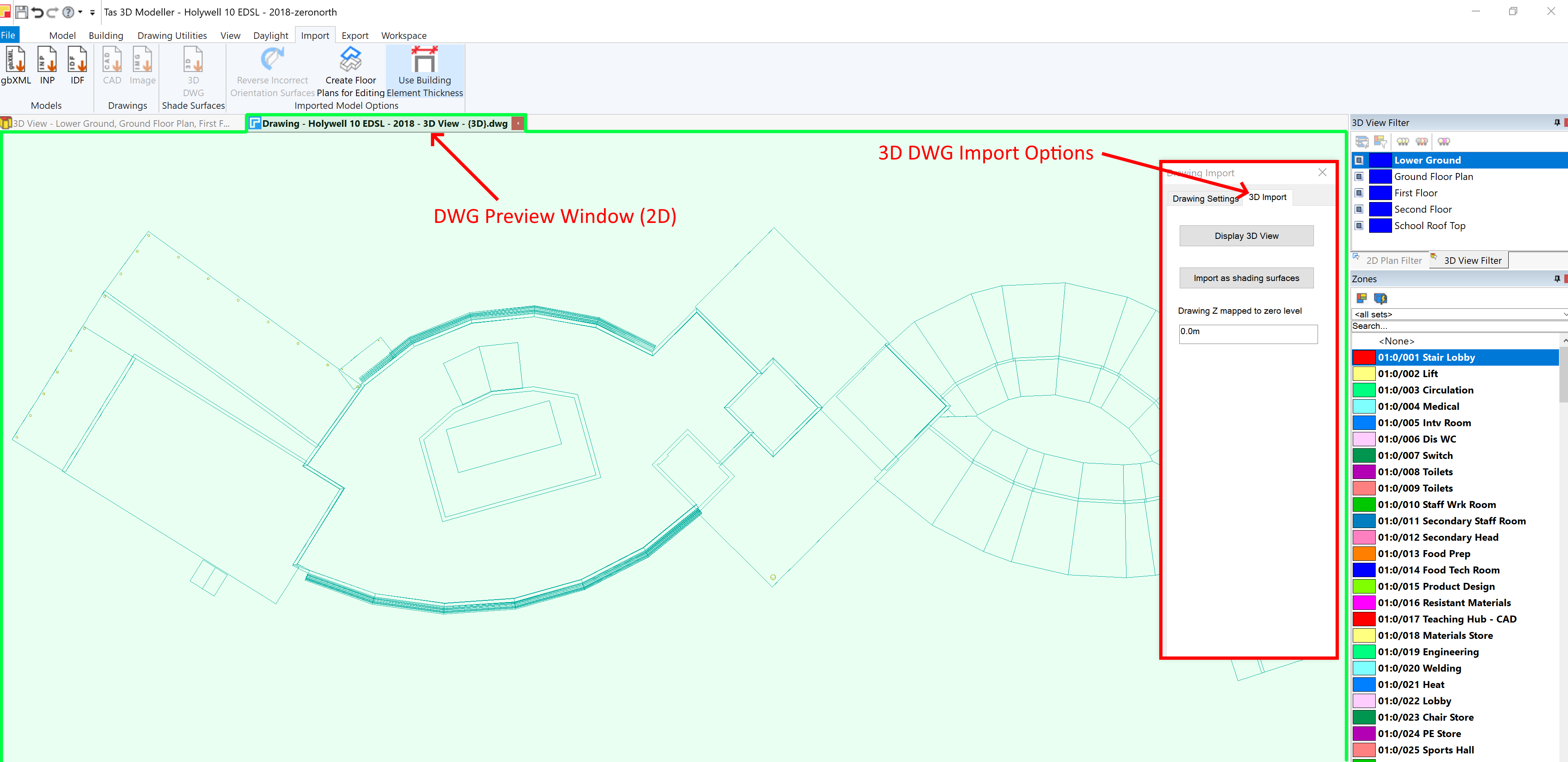
Select the layers you wish to import shade surfaces from on the Drawing Settings tab and then switch to the 3D Import tab to complete the process.
Set the height offset (z-mapping), which is used to adjust the height at which the imported geometry is placed, and press Import as Shading Surfaces to complete the process:
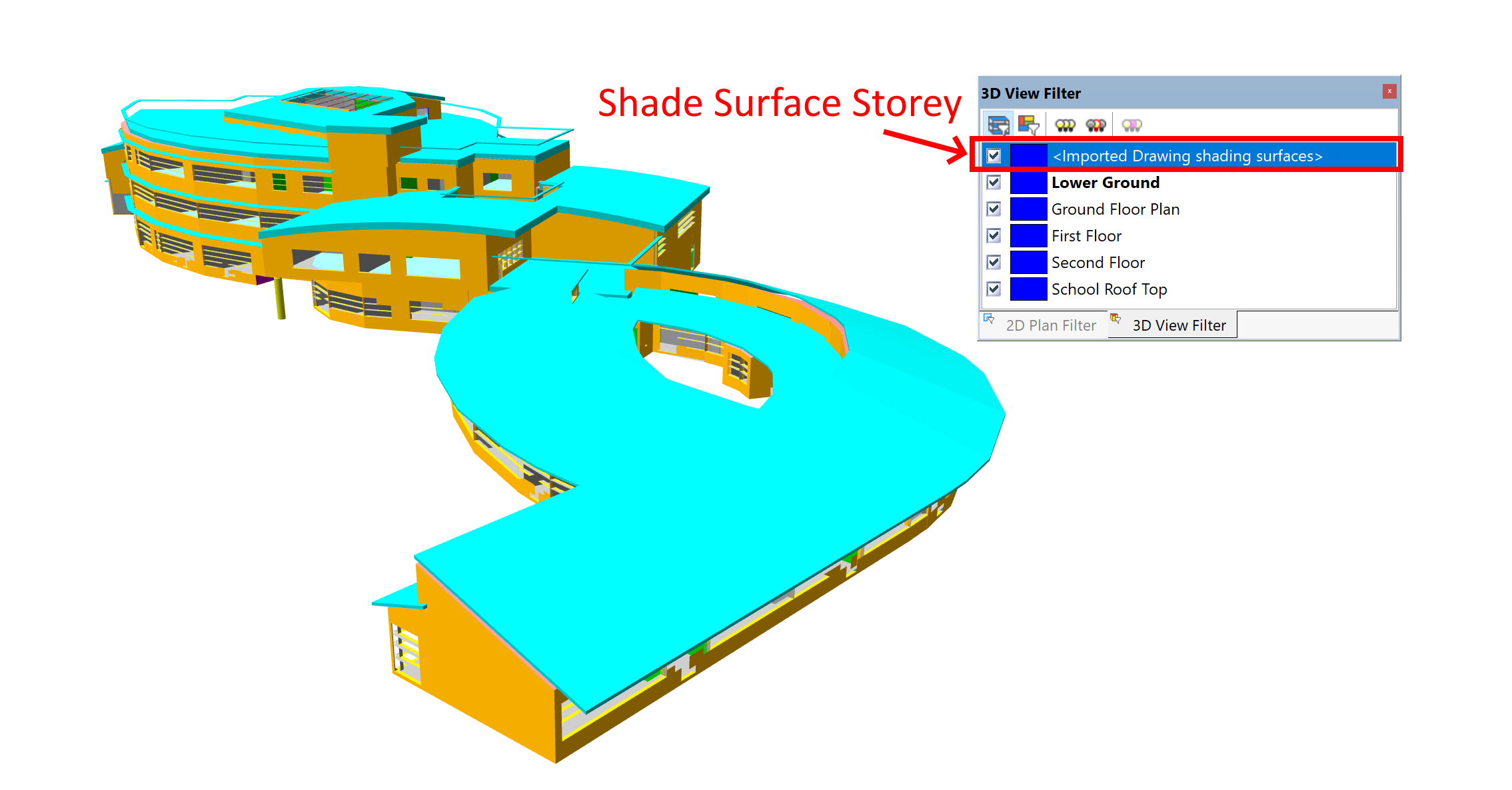
The imported shade surfaces appear on their own storey, and can be removed via the Edit Storeys Dialog.
If you import additional shade surfaces from another 3D DWG, you can choose to either merge these with your existing shade surfaces or replace them:
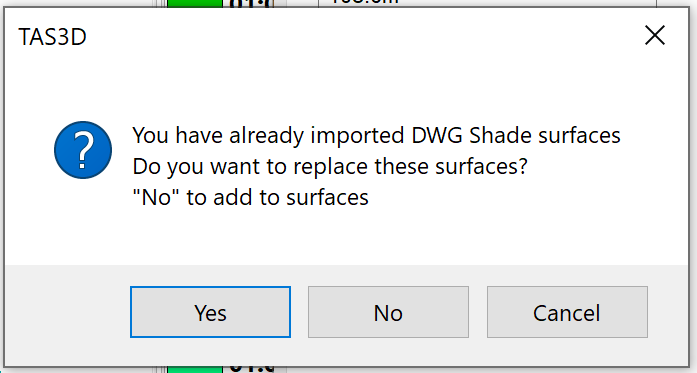
If you merge additional shade surfaces with the existing shade surfaces, they will be placed on the same Storey.